Vol. 7, No. 3, May, 2004. Mathematical and Natural Sciences. Study on Bilinear Scheme and Application to Threedimensional Convective Equation Itaru Hataue and Yosuke. Type or paste a DOI name into the text box. Click Go. Your browser will take you to a Web page URL associated with that DOI name. Send questions or comments to doi. The Gartner Group first used the acronym ERP in the 1990s, thirdparty source needed where it was seen by whom to extend the capabilities of material. Successful Erp Implementation Case Study Pdf Examples' title='Successful Erp Implementation Case Study Pdf Examples' />Managing system landscapes during an SAP ERP 6. By submitting your personal information, you agree that Tech. Target and its partners may contact you regarding relevant content, products and special offers. You also agree that your personal information may be transferred and processed in the United States, and that you have read and agree to the Terms of Use and the Privacy Policy. Managing SAP ERP 6. Upgrade Projects. Chapter 5 Executing an Upgrade Project. How do organizations managing an SAP ERP 6. What can be done to ensure that SAP ERP upgrades run smoothly after completionIn this chapter, Martin Reidel, Senior Vice President of SAPs Global Upgrade Office, discusses the best system landscapes for upgrade projects, as well as why downtime is one of the biggest challenges during an SAP upgrade, and what can be done to minimize downtime during projects. This section lists the factors that you should look at when considering an SAP ERP 6. QAconsolidation and production landscape. Managing SAP ERP 6. Upgrade Projects, Ch. Table of contents Managing system landscapes during SAP ERP 6. How to minimize upgrade downtime during an SAP upgrade project. How should the system landscape be set up during an upgrade project How can downtime be minimized, and what support tools and methods exist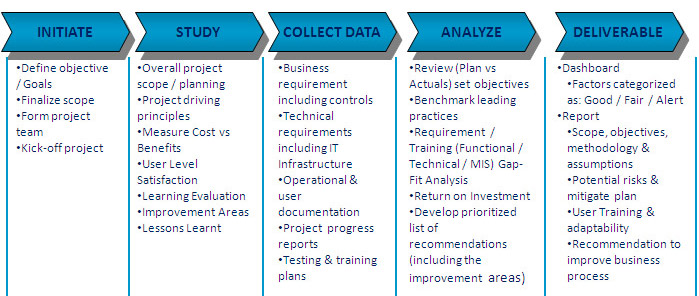 What about training the project team and end users Chapter 5 answers these questions and provides recommendations based on lessons learned from numerous upgrade projects. Chapter 5 Executing an Upgrade Project. This chapter looks at the execution phase of an upgrade. Based on two main upgrade challenges perceived by customers, its focus is on downtime minimization and training. In addition, we will look at system landscape strategies that can help you successfully complete your upgrade project. You can follow several different paths to tackle downtime. We will show you how careful analysis of your situation can help you manage this issue successfully. We will also describe the options offered by SAP to keep downtime to a minimum. The section on a recommended system landscape outlines a recommendation for how to set up and manage your system landscape in an upgrade project. It is not feasible within the scope of this book to show all possible system landscapes, as each is customer specific. However, it is instructive to examine and understand a basic setup that shows how the system landscape evolves throughout the project. From this, you can begin to analyze your own system landscape and take the necessary measures to build the appropriate environment specific to your requirements. When planning to tackle an upgrade, it will most likely become apparent a knowledge gap exists for many of your staff, either on the technical side or in terms of the functionality that will be implemented. In the section on training, you will find numerous recommendations for determining the training your organization will need as well as suggestions for relevant SAP courses. Finally, we will look at some of the lessons learned from upgrade projects. These will give you insight into what makes a successful project, based on real experience from SAPs involvement in numerous upgrade projects. Install Nissan Fast Software. Managing the System Landscape During an Upgrade Project. The goal of this section is to provide guidance and recommendations for a standard three system SAP customer landscape however, it cannot fully explore all of the potential additional systems and interdependencies you might have in your specific landscape. The code freeze strategy. The technical availability of hardware for setting up temporary systems during the project sandbox and training systems. The operational ease of setting up sandbox systems, shadow systems, and so on in your IT environment or with your hosting service provider. Depending on the scope of the upgrade, your upgrade project can last several months. During this time, it is often inevitable that you will need to make at least some changes to the production system. For many customers, it is not possible to expect the business to suspend all changes to the system during that time. Therefore, you must define an appropriate change management strategy that will restrict and regulate changes to the production system within the context of the system landscape you are using for upgrade testing and project refinement. The code freeze period will usually start after the development system has been established. From that point in time, double maintenance of coding and other system configuration changes is necessary. At a point close to the cutover weekend usually after the final integration testing at the latest, you will also have to define a hard code freeze strategy which restricts transports even more and allows only the most urgent of changes to be implemented. Lego City Undercover Pc Game Demo. Section 4. 4, Best Practices, in Chapter 4, provides a recommendation for a code freeze strategy. You should also consider the need to set up separate systems for training purposes, interface testing, modification adjustments, and custom developments. Most customers, however, will use a three tier system landscape with an additional sandbox as the playground for the upgrade project. Recommended System Landscape. This section provides you with recommendations on how to set up your system to minimize upgrade risks and minimize the duration of the code freeze period. The examples show a typical three system landscape, consisting of a development system, a quality assuranceconsolidation system, and a production system. The recommendations show how additional copies of these systems are used to perform required activities during the upgrade project such as adjusting custom developments and testing. We will look at how the systems evolve during the different phases of the upgrade project Project preparation. Upgrade blueprint. Upgrade realization. Final preparation for cutover. X Blades Pc Game here. Production cutover go live and support. The scenarios are based on a suggested timeline, which runs over four months. For each phase, each scenario gives a suggested duration, in weeks. The recommendations assume that you have the appropriate hardware available for creating additional systems. We describe actual project work, how each system is upgraded to the new release from the old release, and the transport routes required. Recommended project activities are suggested for each team involved at each phase, as follows Project management. The team in charge of the upgrade project that manages all activities that are part of the project. Technical. The IT team that manages the system technology such as hardware, the operating system, and database software. Development. The software development team responsible for custom developments and modifications to the core SAP software. Business experts. Experts from the organizations business units who understand the business processes and how SAP functionality is used within each process. Although the system landscape shown in Figure 5. SAP R3 4. 6. C to SAP ERP 6. SAP R3 releases. The main objective is to show how the system evolves with systems running either the source or the target release, culminating in an upgraded production system. Project Preparation. Project preparation is the first phase of the project, where initial work is done on an upgraded copy of the production system. The project management team must first arrange for an upgrade project system to be available.
What about training the project team and end users Chapter 5 answers these questions and provides recommendations based on lessons learned from numerous upgrade projects. Chapter 5 Executing an Upgrade Project. This chapter looks at the execution phase of an upgrade. Based on two main upgrade challenges perceived by customers, its focus is on downtime minimization and training. In addition, we will look at system landscape strategies that can help you successfully complete your upgrade project. You can follow several different paths to tackle downtime. We will show you how careful analysis of your situation can help you manage this issue successfully. We will also describe the options offered by SAP to keep downtime to a minimum. The section on a recommended system landscape outlines a recommendation for how to set up and manage your system landscape in an upgrade project. It is not feasible within the scope of this book to show all possible system landscapes, as each is customer specific. However, it is instructive to examine and understand a basic setup that shows how the system landscape evolves throughout the project. From this, you can begin to analyze your own system landscape and take the necessary measures to build the appropriate environment specific to your requirements. When planning to tackle an upgrade, it will most likely become apparent a knowledge gap exists for many of your staff, either on the technical side or in terms of the functionality that will be implemented. In the section on training, you will find numerous recommendations for determining the training your organization will need as well as suggestions for relevant SAP courses. Finally, we will look at some of the lessons learned from upgrade projects. These will give you insight into what makes a successful project, based on real experience from SAPs involvement in numerous upgrade projects. Install Nissan Fast Software. Managing the System Landscape During an Upgrade Project. The goal of this section is to provide guidance and recommendations for a standard three system SAP customer landscape however, it cannot fully explore all of the potential additional systems and interdependencies you might have in your specific landscape. The code freeze strategy. The technical availability of hardware for setting up temporary systems during the project sandbox and training systems. The operational ease of setting up sandbox systems, shadow systems, and so on in your IT environment or with your hosting service provider. Depending on the scope of the upgrade, your upgrade project can last several months. During this time, it is often inevitable that you will need to make at least some changes to the production system. For many customers, it is not possible to expect the business to suspend all changes to the system during that time. Therefore, you must define an appropriate change management strategy that will restrict and regulate changes to the production system within the context of the system landscape you are using for upgrade testing and project refinement. The code freeze period will usually start after the development system has been established. From that point in time, double maintenance of coding and other system configuration changes is necessary. At a point close to the cutover weekend usually after the final integration testing at the latest, you will also have to define a hard code freeze strategy which restricts transports even more and allows only the most urgent of changes to be implemented. Lego City Undercover Pc Game Demo. Section 4. 4, Best Practices, in Chapter 4, provides a recommendation for a code freeze strategy. You should also consider the need to set up separate systems for training purposes, interface testing, modification adjustments, and custom developments. Most customers, however, will use a three tier system landscape with an additional sandbox as the playground for the upgrade project. Recommended System Landscape. This section provides you with recommendations on how to set up your system to minimize upgrade risks and minimize the duration of the code freeze period. The examples show a typical three system landscape, consisting of a development system, a quality assuranceconsolidation system, and a production system. The recommendations show how additional copies of these systems are used to perform required activities during the upgrade project such as adjusting custom developments and testing. We will look at how the systems evolve during the different phases of the upgrade project Project preparation. Upgrade blueprint. Upgrade realization. Final preparation for cutover. X Blades Pc Game here. Production cutover go live and support. The scenarios are based on a suggested timeline, which runs over four months. For each phase, each scenario gives a suggested duration, in weeks. The recommendations assume that you have the appropriate hardware available for creating additional systems. We describe actual project work, how each system is upgraded to the new release from the old release, and the transport routes required. Recommended project activities are suggested for each team involved at each phase, as follows Project management. The team in charge of the upgrade project that manages all activities that are part of the project. Technical. The IT team that manages the system technology such as hardware, the operating system, and database software. Development. The software development team responsible for custom developments and modifications to the core SAP software. Business experts. Experts from the organizations business units who understand the business processes and how SAP functionality is used within each process. Although the system landscape shown in Figure 5. SAP R3 4. 6. C to SAP ERP 6. SAP R3 releases. The main objective is to show how the system evolves with systems running either the source or the target release, culminating in an upgraded production system. Project Preparation. Project preparation is the first phase of the project, where initial work is done on an upgraded copy of the production system. The project management team must first arrange for an upgrade project system to be available.